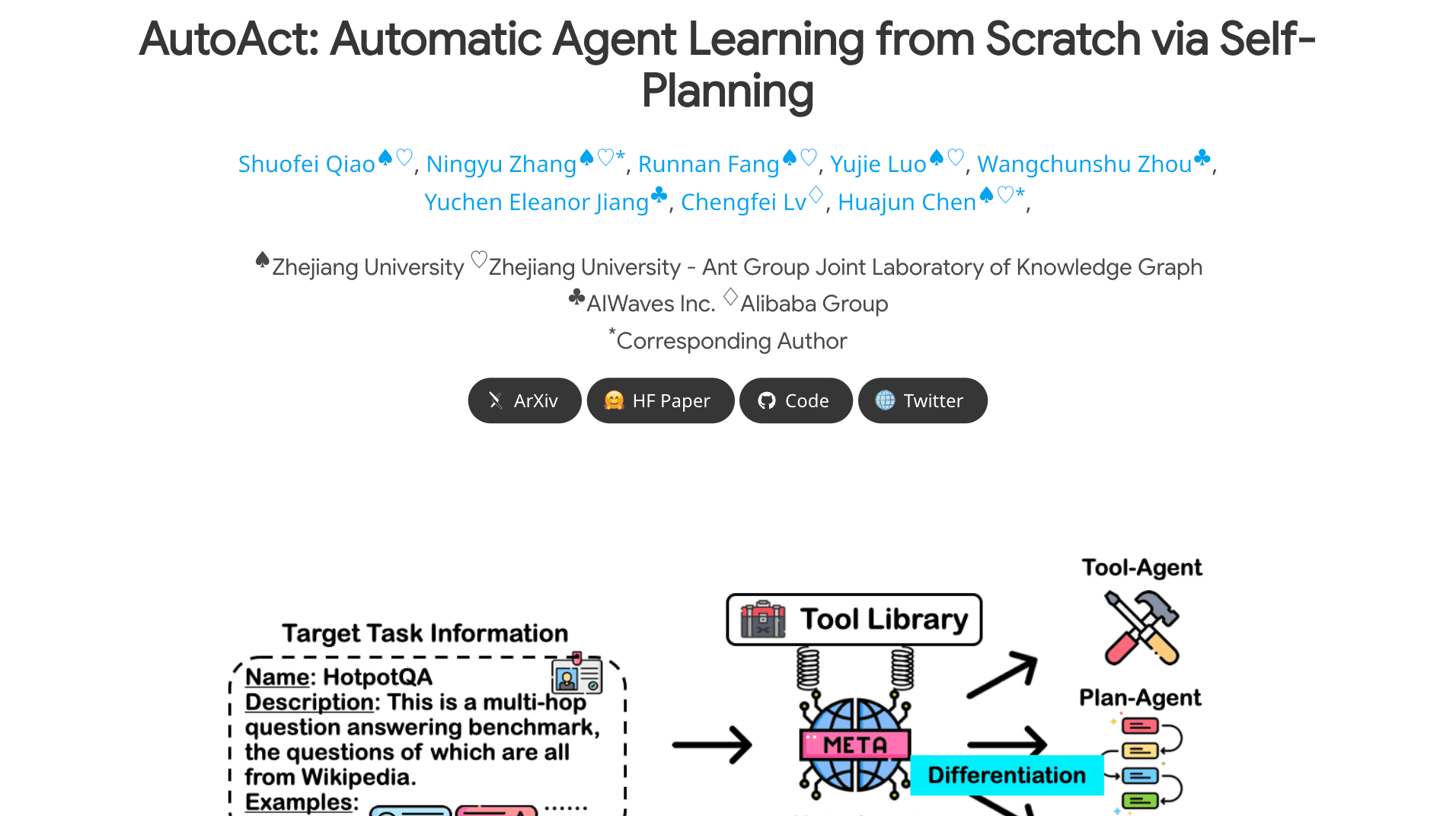

AutoAct
Automatic Agent Learning from Scratch via Self-Planning
Autonomous AI agent for complex workflows. Build intelligent automation.


Automatic Agent Learning from Scratch via Self-Planning
Autonomous AI agent for complex workflows. Build intelligent automation.
Claude API for developers and enterprises
Autonomous AI agent for complex workflows. Build intelligent automation.
Unified AI platform for building and deploying ML models
Autonomous AI agent for complex workflows. Build intelligent automation.
Enterprise AI platform for building and deploying LLM applications
Autonomous AI agent for complex workflows. Build intelligent automation.
Launch your SaaS in days, not months
Next.js SaaS boilerplate with AI integration and auth. Authentication, Stripe payments, database included. Launch production SaaS startups 10x faster.
Buy and sell micro SaaS businesses
Productivity tool powered by AI. Work smarter, not harder.
Build custom AI agents with no code
AI writing tool for better content. Join writers saving hours daily.
Turn videos into 27 pieces of content instantly
AI video tool for content creators. Make videos 10x faster.
Collect and display customer testimonials with AI
Powerful AI tool to boost productivity. Compare & discover alternatives.
Create ultra-realistic AI voices and speech
Powerful AI tool to boost productivity. Compare & discover alternatives.
AI SEO Content Writer
AI writing tool for better content. Join writers saving hours daily.
Find your dream remote job without the hassle
Productivity tool powered by AI. Work smarter, not harder.



After months with Claude Code, I've discovered six strategies that reliably work. Forget autonomous loops - here's what actually works for production code.
Super Bowl AI ads signal the bubble's end. Companies burning billions in losses are desperately trying to stave off the inevitable crash - just like 2000.



I tested Ampcode on production refactors for a month. It's faster than Claude Code for big changes, but requires careful review. Here's what I learned.
AI-powered search, summaries, and automation for Slack
AI-powered meeting assistant for productivity and collaboration
All-in-one AI platform for creating courses, communities, and branded websites
Create landing pages, funnels, and courses from one prompt with AI
Detailed conversation insight summaries
Meeting minutes and task extraction
Meta enhanced meeting assistant
Meeting analytics, emotion detection, and summaries
Transform photos into AI art - Ghibli anime, sketches, and custom styles in seconds
Design Anything, Publish Anywhere
3D Editing Tool
Design Tool
AI Image Editor
AI-powered creative suite for photo and video
Capture and create photorealistic 3D with AI
AI-generated game assets in your art style
AI model that creates realistic and imaginative video from text
Create & Share Videos That Convert
AI Task Manager & Calendar Optimizer
AI video generation for everyone
Transform videos into immersive 3D environments
AI video repurposing for social media
AI video and voice generation platform
Professional AI voice and video presentation platform
Markerless motion capture powered by AI
Turn scripts into videos automatically
AI video generation for creative expression
AI video repurposing for short-form content