If you've used ChatGPT, Claude, or any other AI chatbot recently, you've interacted with a Large Language Model (LLM). These sophisticated AI systems can write essays, debug code, answer questions, and even engage in creative storytelling. But how do these digital minds actually work?
Let's pull back the curtain and explore the fascinating journey from raw text to intelligent conversation.
The Four-Stage Journey of an LLM
Building an LLM is like teaching someone a new language, except your student is a massive neural network and your classroom is the entire internet. The process breaks down into four distinct stages, each building upon the last.
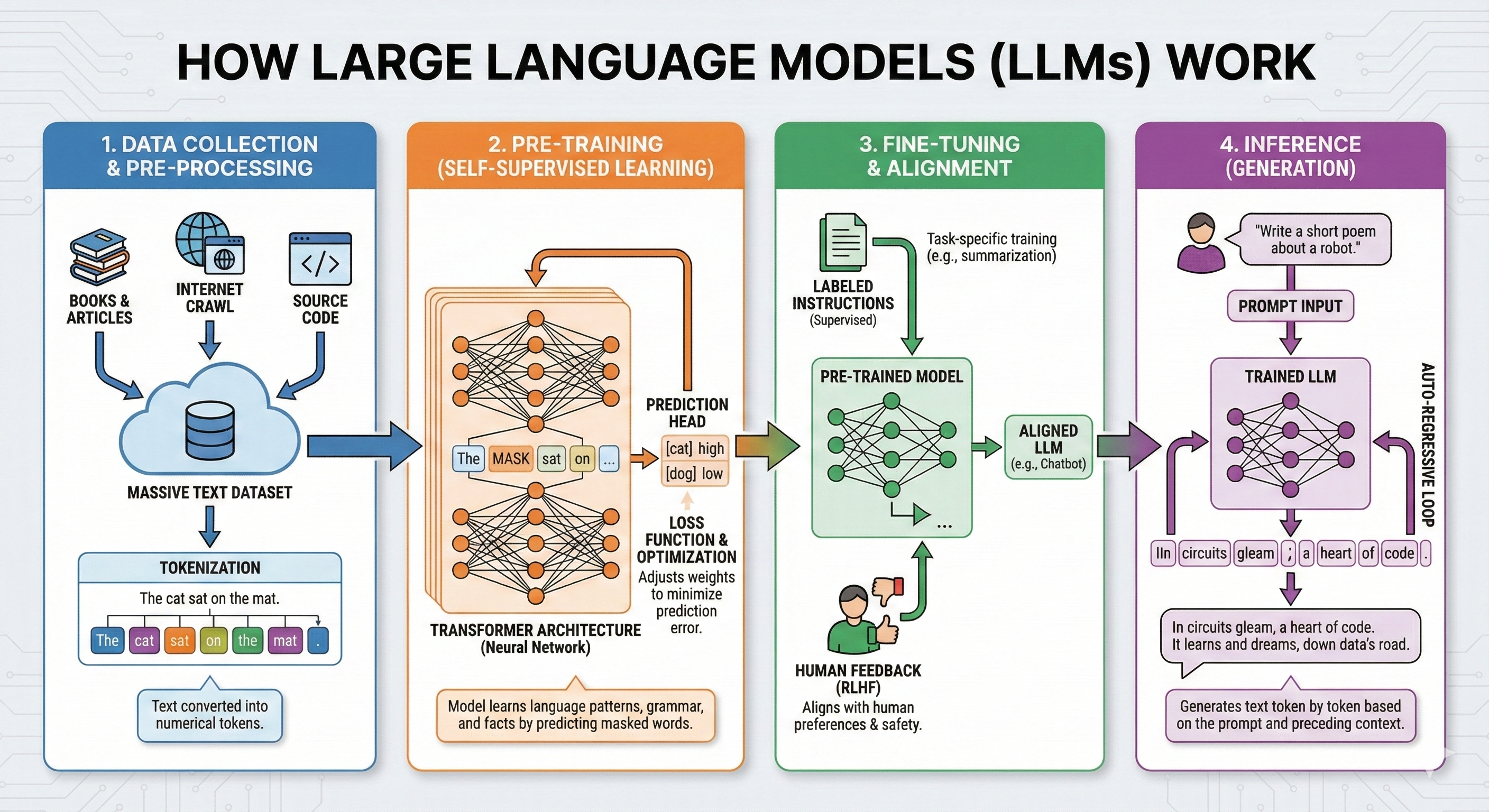
Stage 1: Data Collection & Pre-Processing – Building the Foundation
Before an LLM can learn anything, it needs data. Lots of it.
Gathering the Raw Materials
The first stage involves collecting massive amounts of text from diverse sources:
- Books & Articles: Classic literature, scientific papers, news articles, and more provide structured, high-quality language examples
- Internet Crawls: Web scraping captures the breadth of human knowledge and conversation styles across billions of web pages
- Source Code: Programming languages and code repositories help models understand logical structures and technical syntax
This raw text is then stored in a massive dataset, often containing hundreds of billions of words.
From Words to Numbers: Tokenization
Here's where things get interesting. Computers don't understand words the way we do-they need numbers. Through a process called tokenization, text is broken down into smaller units called tokens and converted into numerical representations.
For example, the sentence "The cat sat on the mat" might be split into tokens like: ["The", "cat", "sat", "on", "the", "mat", "."], with each token assigned a unique numerical ID.
This numerical representation allows the neural network to process language mathematically.
Stage 2: Pre-Training – Learning the Patterns of Language
This is where the magic begins. During pre-training, the model learns to understand language through a clever technique called self-supervised learning.
The Masked Word Game
Imagine playing a game where random words in sentences are hidden, and you have to guess what they are:
"The cat [MASK] on the mat."
You'd probably guess "sat," right? That's essentially what the model does-but billions of times.
The Transformer Architecture
At the heart of modern LLMs is the Transformer architecture, a type of neural network specifically designed for processing sequences of data. Think of it as a complex web of interconnected nodes, each learning to recognize patterns at different levels:
- Some nodes learn basic grammar rules
- Others recognize common phrases and idioms
- Deeper layers understand context, tone, and semantic relationships
The Learning Process
The model is shown a sentence with masked words and tries to predict which words should fill those positions. When it guesses wrong, a loss function measures how far off its prediction was, and an optimization algorithm adjusts the neural network's internal weights to improve future predictions.
Through this process repeated trillions of times across massive datasets, the model gradually learns:
- Vocabulary and word relationships
- Grammar and syntax
- Facts about the world
- Common patterns in human communication
By the end of pre-training, you have a base model that understands language structure and can generate coherent text-but it's not quite ready for prime time yet.
Stage 3: Fine-Tuning & Alignment – Teaching It to Be Helpful
A pre-trained model is like a brilliant student who knows everything about language but doesn't quite know how to have a proper conversation. That's where fine-tuning comes in.
Supervised Task-Specific Training
First, the model undergoes supervised learning with labeled examples of desired behavior:
- "Here's a good summary of this article."
- "This is how you answer a technical question."
- "This is an appropriate response to a user request."
Human experts create these training examples, showing the model what high-quality, helpful responses look like.
RLHF: Learning from Human Preferences
The real breakthrough in modern LLMs came with Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). Here's how it works:
- The model generates multiple responses to the same prompt
- Human evaluators rank these responses from best to worst
- The model learns to prefer responses similar to the highly-ranked ones
This process helps the model understand nuanced concepts like:
- Helpfulness vs. harm
- Accuracy vs. speculation
- Appropriate vs. inappropriate content
- When to admit uncertainty
The result is an aligned LLM-a model that not only understands language but also behaves in ways that are safe, helpful, and aligned with human values.
Stage 4: Inference – Putting It All to Work
Finally, we arrive at what you experience as a user: inference, or generation.
From Prompt to Response
When you type a prompt like "Write a short poem about a robot," here's what happens behind the scenes:
- Tokenization: Your prompt is converted into numerical tokens
- Context Processing: The trained LLM processes these tokens through its neural network
- Token-by-Token Generation: The model predicts the next most likely token, then the next, and the next, building the response word by word
- Auto-Regressive Loop: Each newly generated token becomes part of the context for predicting the subsequent token
The Poetry of Probability
The model doesn't simply retrieve pre-written answers-it genuinely creates text by predicting the most probable next word based on:
- The prompt you provided
- The conversation history
- Everything it learned during training
When you receive a response like "In circuits gleam, a heart of code. It learns and dreams, down data's road," the model generated this token by token, weighing countless probability distributions at each step.
The Bigger Picture
Understanding how LLMs work helps us appreciate both their capabilities and limitations:
What They Excel At
- Pattern recognition in language
- Generating coherent, contextually appropriate text
- Synthesizing information from their training data
- Following instructions and adapting to different tasks
What They Struggle With
- Reasoning about events after their training cutoff
- Performing precise mathematical calculations
- Understanding physical causality
- Maintaining perfect consistency across long conversations
The Future of Language AI
The field of LLMs is evolving rapidly. Current research focuses on:
- Scaling: Larger models with more parameters and training data
- Efficiency: Smaller models that perform as well as larger ones
- Multimodality: Models that understand images, audio, and video alongside text
- Reasoning: Enhanced ability to think through complex problems step-by-step
- Personalization: Models that adapt to individual users while respecting privacy
Conclusion
Large Language Models represent one of the most significant advances in artificial intelligence. From collecting trillions of words to learning language patterns, from alignment with human values to generating helpful responses, the journey from raw data to conversational AI is both technically sophisticated and conceptually elegant.
The next time you interact with an LLM, you'll know the remarkable engineering and training process behind that simple text box. These models aren't just databases of information-they're statistical systems that learned to understand and generate human language by studying patterns across nearly all human written knowledge.
And we're just getting started.
Want to dive deeper into AI and language models? Check out our AI tools directory for the latest AI-powered solutions, or explore our other blog posts on machine learning and the future of AI technology.